
Optimal Soil for Thriving Hydrangeas: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover the best soil for growing healthy hydrangeas. Learn how to create optimal soil conditions and maintain them for vibrant blooms.
Read MoreYou can download a PowerPoint summary of the full article (Diatomaceous Earth for Hydrangeas) here, which includes proper source attribution and is freely shareable and usable: Download PPTX Summary
You can download a PDF summary of the full article (Diatomaceous Earth for Hydrangeas) here, which includes proper source attribution and is freely shareable and usable: Download PDF Summary
Diatomaceous earth (DE) is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous sedimentary rock that can be crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It is composed of the fossilized remains of diatoms, a type of microscopic algae with silica-based cell walls. Over millions of years, these diatoms accumulated in aquatic environments, forming extensive deposits that are mined for various uses today.
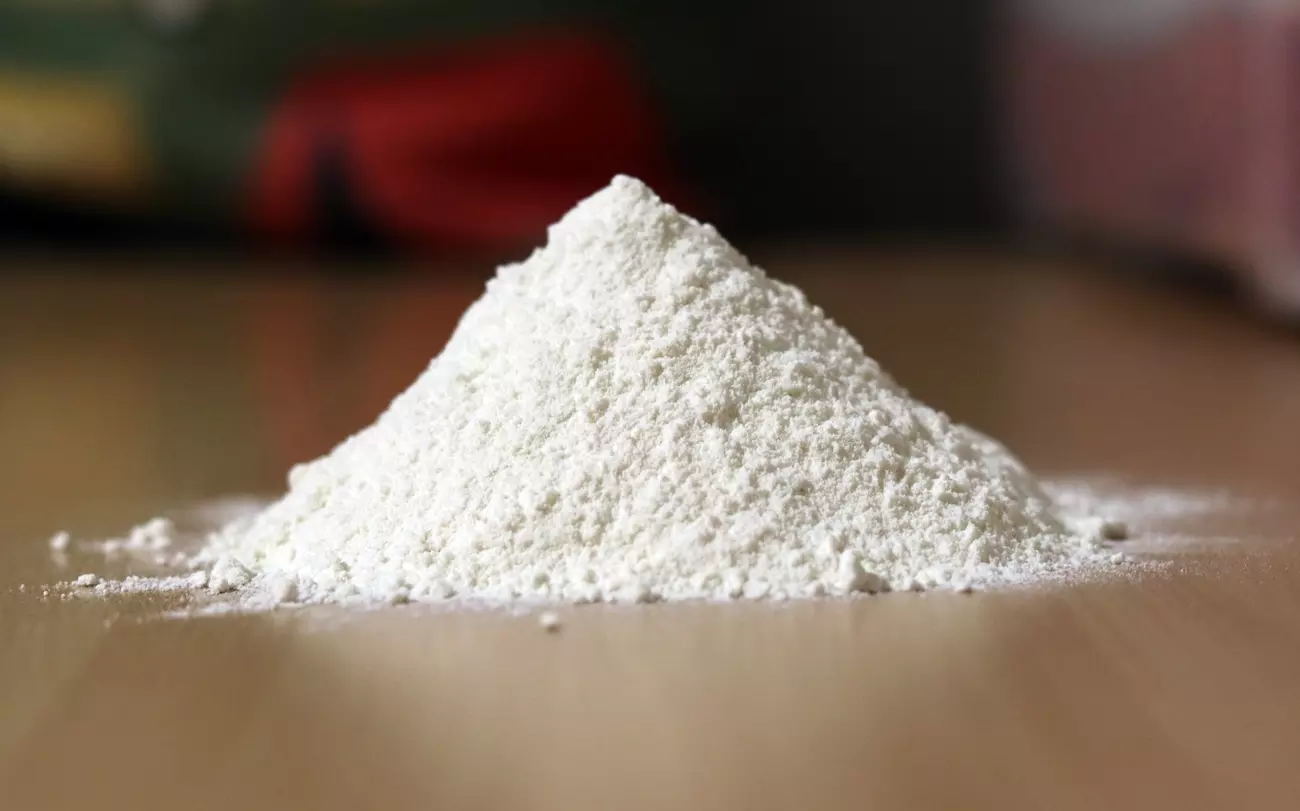

The primary component of diatomaceous earth is silica, making up approximately 80–90% of its composition. Other constituents include alumina (2–4%) and iron oxide (0.5–2%). The material is highly porous, giving it a low density and significant absorptive capacity. Its abrasive texture is due to the microscopic, sharp edges of the diatom remains.
Diatomaceous earth forms from the accumulation and fossilization of diatom skeletons in sedimentary layers over geological timescales. These deposits are typically found in ancient lake beds and marine environments. Significant deposits have been identified and mined in various parts of the world, including the United States and Europe.
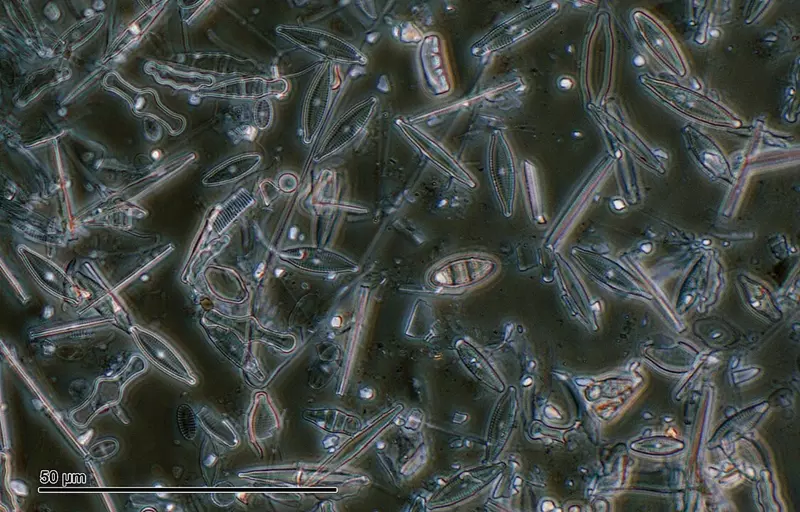
Diatomaceous earth has a wide range of applications across various industries due to its unique properties:
While diatomaceous earth is generally considered safe for various uses, certain precautions are necessary:
It is essential to use the appropriate grade of diatomaceous earth for specific applications and to follow safety guidelines to minimize health risks.
Diatomaceous earth is a natural and abundant resource. Its use as an insecticide offers an eco-friendly alternative to chemical pesticides, reducing environmental contamination. However, it can also affect non-target organisms, including beneficial insects, so careful application is necessary to mitigate unintended impacts.
Diatomaceous earth is a versatile material with a broad spectrum of applications, from industrial filtration to natural pest control. Understanding its properties, uses, and safety considerations is essential for effective and responsible utilization.
Diatomaceous earth (DE) serves as an effective, natural insecticide for hydrangeas. Its abrasive particles damage the exoskeletons of pests like aphids, slugs, and spider mites, leading to their dehydration and death. This method offers a chemical-free alternative for managing garden pests.

Incorporating DE into the soil enhances its structure by increasing porosity. This improvement facilitates better root development and nutrient uptake in hydrangeas, promoting healthier growth.
The porous nature of DE allows it to absorb and retain moisture, ensuring that hydrangeas receive consistent hydration. This quality is particularly beneficial during dry periods, helping to maintain soil moisture levels.
DE contains essential minerals such as silica, calcium, magnesium, and iron, which contribute to the overall health and vitality of hydrangeas. These nutrients support robust plant development and flowering.
Utilising DE in your garden aligns with sustainable practices by reducing reliance on chemical pesticides and fertilisers. Its natural composition makes it safe for the environment, humans, and pets when used appropriately.
Incorporating diatomaceous earth into your hydrangea care routine offers multiple benefits, from natural pest control to improved soil health. By following proper application methods and safety precautions, you can enhance the growth and vitality of your hydrangeas while promoting an eco-friendly garden environment.
Applying diatomaceous earth to hydrangeas offers several advantages:
There are two primary methods for applying diatomaceous earth to hydrangeas:
Diatomaceous earth offers an effective, natural method for protecting hydrangeas from pests. By following appropriate application techniques and safety measures, gardeners can enhance the health and vitality of their hydrangeas while adhering to eco-friendly practices.
Applying diatomaceous earth to hydrangeas offers several advantages:
There are two primary methods for applying diatomaceous earth to hydrangeas:
Diatomaceous earth offers an effective, natural method for protecting hydrangeas from pests. By following appropriate application techniques and safety measures, gardeners can enhance the health and vitality of their hydrangeas while adhering to eco-friendly practices.
Hydrangeas, cherished for their vibrant blooms, can fall victim to various pests that compromise their health and aesthetics. Identifying these common culprits is the first step in effective pest management.
Employing a combination of cultural, mechanical, biological, and chemical controls offers a holistic approach to managing hydrangea pests.
Regular inspection of hydrangeas is crucial for early pest detection and management.
Implementing preventative strategies can reduce the likelihood of pest infestations.
Effective pest control on hydrangeas requires a comprehensive approach that includes proper cultural practices, regular monitoring, and the judicious use of mechanical, biological, and chemical controls. By maintaining plant health and promptly addressing pest issues, gardeners can enjoy the full beauty of their hydrangeas throughout the growing season.
For a visual guide on identifying and managing common hydrangea pests, consider watching the following video tutorial:
Incorporating diatomaceous earth into garden soil offers several advantages:
To effectively utilise diatomaceous earth for soil enhancement, consider the following application methods:
Integrating diatomaceous earth into your gardening practices can significantly enhance soil quality, leading to healthier plant growth and improved yields. By understanding its benefits and adhering to proper application methods, gardeners can create an optimal growing environment for their plants.
When handling diatomaceous earth, it's crucial to protect yourself from potential irritations:
To ensure effective and safe use of diatomaceous earth on hydrangeas:
While diatomaceous earth is a natural product, it's important to use it responsibly:
Proper storage and disposal of diatomaceous earth are essential to maintain its effectiveness and minimise risks:
In case of accidental exposure:
Diatomaceous earth can be a valuable tool in maintaining the health of your hydrangeas when used correctly. By following these safety precautions, you can protect yourself, your plants, and the environment, ensuring a safe and effective gardening experience.
Diatomaceous earth (DE) is a naturally occurring, silica-rich sedimentary rock composed of the fossilised remains of diatoms, a type of microscopic algae. When ground into a fine powder, DE is widely used in pest control, soil enhancement, and other gardening applications.
DE works as a mechanical insecticide by adhering to insects’ exoskeletons. Its abrasive particles damage their protective outer layer, causing dehydration and eventual death. This non-toxic method is particularly effective against crawling pests such as ants, slugs, and aphids.
Food-grade DE is generally safe for humans and pets when used appropriately. However, inhalation of DE dust can irritate the respiratory system. It is recommended to wear a mask during application to minimise exposure to airborne particles.
Yes, DE can be used indoors to control pests such as cockroaches, ants, and fleas. Apply a thin layer in cracks, crevices, and areas where pests are active. Ensure the area remains dry, as moisture diminishes DE’s effectiveness.
Lightly dust the soil and plant surfaces with DE using a hand applicator. Focus on the base of the hydrangea and any areas where pests are active. Apply on dry days and reapply after rain or watering to maintain its effectiveness.
DE can harm beneficial insects such as bees and ladybirds if applied to flowers or areas they frequent. To minimise harm, apply DE to the soil and lower parts of plants, avoiding direct application to blooms.
Yes, food-grade DE is safe for gardening and pest control, containing low levels of crystalline silica. Pool-grade DE, on the other hand, is treated with heat and contains high levels of crystalline silica, making it hazardous for use around humans, pets, and plants.
DE remains effective as long as it remains dry. Its effectiveness diminishes in wet or humid conditions, so reapplication may be necessary after rain or watering. Proper storage in a sealed container ensures its long-term usability.
Yes, sprinkling DE in compost can help manage pests and improve aeration. Mix it evenly into the compost to distribute its benefits while ensuring it does not accumulate in clumps.
Food-grade DE is approved for use in organic gardening as a natural pest control method. Its non-toxic properties make it a safe alternative to chemical pesticides.
Store DE in a tightly sealed container in a cool, dry place. Keeping it away from moisture ensures its effectiveness remains intact for future use. Label the container clearly to prevent accidental misuse.
DE does not have an expiry date if stored properly. Its effectiveness can last indefinitely as long as it is kept dry and uncontaminated.
Diatomaceous earth is a versatile, eco-friendly solution for maintaining healthy hydrangeas. From pest control to soil enhancement, its benefits are numerous. By following proper application techniques and safety guidelines, you can enjoy thriving, pest-free hydrangeas in your garden.

Discover the best soil for growing healthy hydrangeas. Learn how to create optimal soil conditions and maintain them for vibrant blooms.
Read More
Learn when and how to prune your hydrangeas this spring with our detailed guide. Includes tips for tool preparation and proper pruning techniques.
Read More
A comprehensive month-by-month hydrangea care calendar to ensure your plants thrive throughout the year.
Read More